IHC・ISH試薬 Molecular Diagnostics Division
保管温度2~8℃
用手法用 ヒストステイナー用 ヒストステイナーAT用
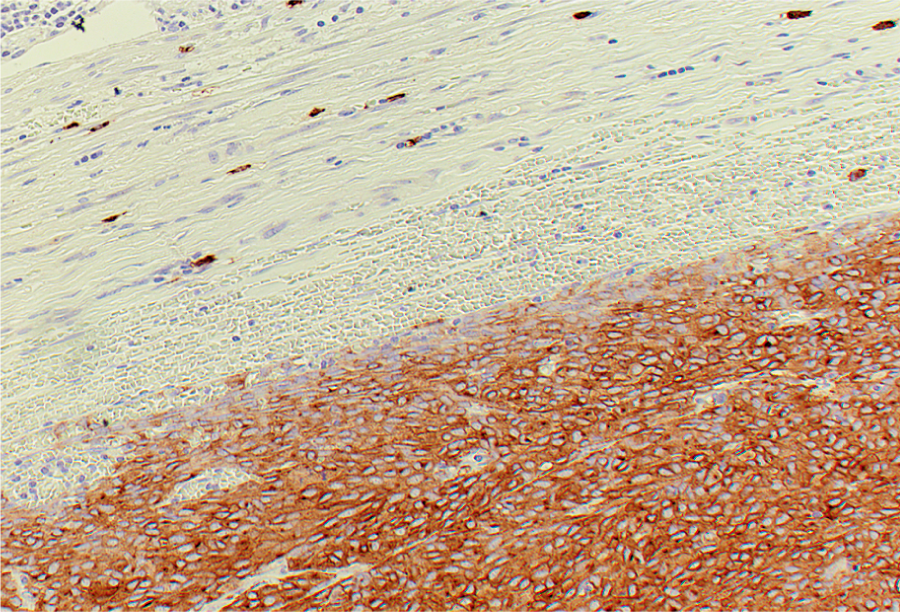
c-KITCD117
■動物種:ウサギ
■使用目的:組織・細胞中のヒトc-kit遺伝子産物の染色。GISTの判別に有用。研究用としてのみ使用すること。
スクロールで確認できます→
用手法用
ヒストステイナー用
ヒストステイナーAT用
※弊社へお問い合わせください
特異性及び抗原分布
ヒトc-kit遺伝子産物(分子量145kDa)と特異的に反応する。c-kit遺伝子産物はSCF(Stem cell Factor)のレセプターであり、結合することにより未分化造血前駆細胞の増殖と分化、肥満細胞の増殖誘導、メラノサイトや生殖細胞の移動や分化が認められる。c-kit遺伝子産物は、肥満細胞やCajalの介在細胞(Interstitial cells of Cajal;ICCs)由来と考えられている消化管のGIST (Gastrointestinal stromal tumor)、精上皮腫/未分化胚細胞腫や肥満細胞由来腫瘍の大部分および悪性黒色腫や肺癌の一部などで発現がみられる。正常では、肥満細胞や精細管、乳管上皮、胃の壁細胞、神経膠細胞、メラノサイトの一部に発現がみられる。
文献
(1) Matsuda R, et al. Expression of the c-kit protein in human solid tumors and in corresponding fetal and adult normal tissues. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):339-46.
(2) Tsuura Y, et al. Preferential localization of c-kit product in tissue mast cells, basal cells of skin, epithelial cells of breast, small cell lung carcinoma and seminoma/dysgerminoma in human: immunohistochemical study on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Virchows Arch. 1994;424(2):135-41.
(3) Yamataka A, et al. A lack of intestinal pacemaker (c-kit) in aganglionic bowel of patients with Hirschsprung's disease. J Pediatr Surg. 1995 Mar;30(3):441-4.
(4) Yamataka A, et al. Lack of intestinal pacemaker (C-KIT-positive) cells in infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 1996 Jan;31(1):96-8; discussion 98-9.
(5) Yamataka A, et al. Localization of intestinal pacemaker cells and synapses in the muscle layers of a patient with colonic hypoganglionosis. J Pediatr Surg. 1996 Apr;31(4):584-7.
(6) Yamataka A, et al. Intestinal pacemaker C-KIT+ cells and synapses in allied Hirschsprung's disorders. J Pediatr Surg. 1997 Jul;32(7):1069-74.
(7) Arber DA, et al. Paraffin section detection of the c-kit gene product (CD117) in human tissues: value in the diagnosis of mast cell disorders. Hum Pathol. 1998 May;29(5):498-504.
(8) Kindblom LG, et al. Gastrointestinal pacemaker cell tumor (GIPACT): gastrointestinal stromal tumors show phenotypic characteristics of the interstitial cells of Cajal. Am J Pathol. 1998 May;152(5):1259-69.
(9) Yamataka A, et al. Abnormal distribution of intestinal pacemaker (C-KIT-positive) cells in an infant with chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction. J Pediatr Surg. 1998 Jun;33(6):859-62.
(10) Hirota S, et al. Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 1998 Jan 23;279(5350):577-80.
(11) Ernst SI et al. KIT mutation portends poor prognosis in gastrointestinal stromal/smooth muscle tumors. Lab Invest. 1998 Dec;78(12):1633-6.
(12) Komuro T, et al. Ultrastructural characterization of the interstitial cells of Cajal. Arch Histol Cytol. 1999 Oct;62(4):295-316.
(13) 秋濱 玄 ほか. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor の組織発生及び悪性度の解析. 岩手医誌. 1999;51:381-90.
(14) Natkunam Y, et al. Utility of paraffin section immunohistochemistry for C-KIT (CD117) in the differential diagnosis of systemic mast cell disease involving the bone marrow. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000 Jan;24(1):81-91.
(15) Maeyama H, et al. Familial gastrointestinal stromal tumor with hyperpigmentation: association with a germline mutation of the c-kit gene. Gastroenterology. 2001 Jan;120(1):210-5.

食道


